How to Choose the Right Pressure Transmitter: Types and Selection Guide for Process Automation
Choosing a pressure transmitter shouldn't feel like deciphering a complex catalog. Whether you're an automation engineer, plant supervisor, or purchase manager, this guide helps simplify your decision-making with practical advice, real-world examples, and key considerations tailored for process industries.
Why Pressure Transmitters Are Critical in Industrial Processes
Pressure transmitters are essential for maintaining consistent process control. They measure the pressure of gases or liquids and convert it into an electrical signal—commonly 4–20 mA—that can be read by PLCs, SCADA systems, or DCS platforms.
Across water treatment plants, food factories, pharmaceutical fermenters, and chemical reactors, these devices ensure safety, operational efficiency, and precise automation. The foundation of their success lies in choosing the right type and specifications for your unique process needs.
What is a Pressure Transmitter?
A pressure transmitter is an instrument that detects pressure and sends out an electrical signal proportional to that pressure. It typically consists of a pressure sensor, signal conditioning electronics (amplifier or converter), and an electrical output interface such as 4–20 mA, HART, or Modbus.
These transmitters are widely used across industries such as manufacturing, food and beverage, pharmaceutical, water and wastewater treatment, HVAC, metals and foundries, and renewable energy plants.
Types of Pressure Transmitters and Where to Use Them
Before diving into the selection process, it’s important to understand the main types of pressure transmitters and their common applications.
Step-by-Step Pressure Transmitter Selection Guide
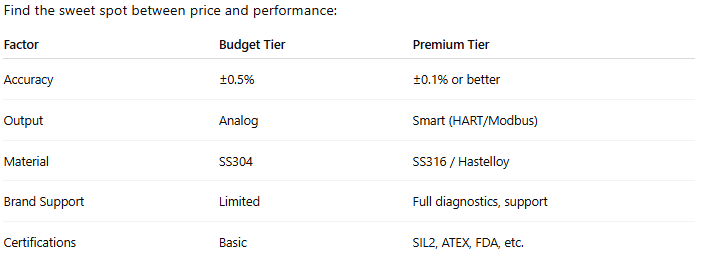
Choosing the wrong transmitter can result in frequent failures, poor data accuracy, and safety concerns. Follow these steps to ensure you select the best-fit device for your application.
Gauge: Common in pipelines and open tanks.
Absolute: Required in vacuum or altitude-sensitive setups.
Differential: Best for filter, flow, or level monitoring in closed systems.
A too-narrow range risks damage from overpressure.
A too-wide range leads to reduced resolution and accuracy.
Step 4: Choose the Right Output Signal
4–20 mA is the industry standard for reliable signal transmission over long distances.
- HART, Modbus, or Profibus are ideal for digital diagnostics, IoT, and smart system integration.Make sure the output format aligns with your control architecture.
Step 5: Select the Appropriate Process Connection
Threaded (NPT/BSP) fittings are common in general industry.
Flanged connections are preferred for high-pressure or large-diameter lines.
Tri-Clamp fittings are best for hygienic applications in food and pharma.
Consider flush diaphragm designs if you're handling viscous or slurry-type fluids.
Step 6: Match Materials with Your Media
SS316 is a safe choice for most clean process fluids.
- For corrosive media, opt for Hastelloy or PTFE linings.Always confirm compatibility to avoid corrosion or sensor failure.
Step 7: Consider Environmental Conditions
Use IP67 or IP68 rated transmitters for outdoor, wet, or dusty environments.
For high-temperature zones, use diaphragm seals or remote mounting setups.
In hazardous areas, choose transmitters with ATEX or IECEx certifications.
Step 8: Plan for Mounting and Maintenance
If the installation point is hard to access, consider remote-mount transmitters with capillary extensions.
Select housings with display windows if local monitoring is required.
Make sure the device allows easy calibration and servicing.
Application-Based Selection Examples
Let Application Requirements Guide the Decision
While it's tempting to go for high-end models based on specs alone, it's best to make choices based on your actual environment and operational goals. At Radical TechMart, we helped a mid-sized food processing company upgrade from a basic gauge transmitter to a smart differential pressure transmitter connected to their SCADA system.
The result was a 27% drop in downtime, real-time filter clog alerts, and improved maintenance efficiency thanks to onboard diagnostics.
Need Help Choosing the Right Model?
Every plant is unique. Instead of guessing, share the following details with our team:
Type of fluid
Pressure range
Desired output signal
Installation location
Required certifications (e.g., FDA, ATEX)
Our instrumentation experts will help you choose the best-suited model from brands like Siemens, WIKA, Yokogawa, and more.
Conclusion
Choosing the right pressure transmitter is more than a technical exercise—it’s a strategic investment. Done right, it enhances process reliability, safety, and productivity.
Use gauge transmitters for general applications
Use absolute transmitters for precision control
Use differential transmitters for advanced feedback
Use multivariable transmitters for intelligent automation
Key Takeaways Recap
Understand your pressure type and range
Match accuracy to the process demands
Align output format with your control system
Confirm process compatibility with materials and connections
Factor in environmental and maintenance needs
Radical TechMart offers curated sensor solutions for every industrial need. Whether you’re working on a new installation or upgrading an old system, we’re here to help you find the perfect fit.